
Due to the nature of the SaaS subscription model, different from one-time purchases of canned software, customers access cloud software services under term contracts. Companies earning revenue from contracts with customers must follow compliance measures when reporting revenue and filing taxes, to avoid penalties. One of the biggest differences between SAAS accounting https://www.bookstime.com/articles/agricultural-accounting and traditional accounting is the way revenue is recognized. In traditional accounting, revenue is recognized all at once when a product is sold. However, in SAAS accounting, revenue is recognized over a period of time (subscription revenue accounting), typically monthly or annually. This is because SAAS businesses provide ongoing services rather than a one-time sale.
The cost of the asset includes the directly attributable costs of preparing the software for its intended use. The balance sheet shows a “snapshot” of the company’s worth and net holdings at the end of the period. The cash flow statement shows how well the company is managing its cash inflows and outflows as compared saas accounting to accrual income for the period. Your bread and butter is likely generated by selling services on a recurring schedule. If you are accepting prepayments, you’ll need to spread out revenue for the duration of your contract. Recognize revenue and expenses in installments throughout the year based on customer usage.
SaaS Accounting – Financial Reporting and Metrics
A SaaS arrangement, like those for platform-as-a-service (PaaS) and infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS), is a cloud computing arrangement. In a software hosting arrangement, a customer obtains access to software hosted by the software vendor (or a third party on its behalf). In some hosting arrangements, the customer’s right to access the hosted software gives rise to a software intangible asset (i.e. a license).
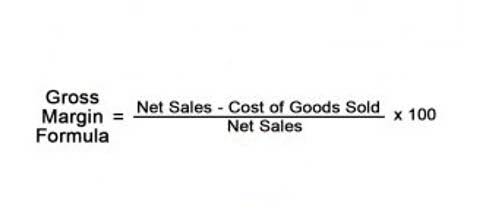
SaaS accounting is the process of managing financial records and transactions for SaaS companies, including tracking revenue, expenses, cash flow, and taxes. While this method is easy to understand and implement, it may not be the best option for SAAS businesses that have a lot of deferred revenue or prepayments. This is because cash-basis accounting does not take into account any revenue that has been earned but not yet received. The first method, cash-basis accounting, is the simplest and most straightforward method. This method involves recognizing income and expenses when they are received or paid, respectively. This means that you only record revenue when you receive payment and expenses when you make a payment.
Deferred Revenue Account In SaaS Accounting
From revenue recognition to SaaS metrics, our SaaS accounting guide covers everything a founder needs to know about accounting for a subscription business. The shift in financial management from traditional methods to Cloud-based solutions has introduced a unique set of challenges and opportunities. That’s why it’s essential to understand the concept and its nuances to effectively manage the finances of a SaaS company. CFOs and their teams need clean, real-time accounting data to properly understand the financial health of the business. It’s the only way to reliably dig into SaaS metrics and glean insights that enable proactive decision-making. But if you and your finance partners are stuck doing everything manually in spreadsheets, you’ll have a tough time embracing your role as strategic business partner.
Leave A Comment